Describe the Structure and Function of Nucleic Acids
Ad Product selection guide for all protein analysis needs. Ad Over 27000 video lessons and other resources youre guaranteed to find what you need.
Nucleic Acids Definition Examples Functions Of Nucleic Acids
They are long-chain polymers that consist of monomeric units called nucleotides.

. Nucleic Acid Structure Readings. Nucleic acids built by polymerizing nucleotides function primarily as informational molecules for the storage and retrieval of information about the primary sequence of polypeptides. Proteins determine how an organisms body is built and how it functions which is why DNA is often.
ACTIVITY 1 Cartoon Make a cartoon or. This intermediate mRNA enters the nucleus of the cell during the synthesis of proteins and bonds with one of the DNA strands. DNA and RNA Comparison.
Start studying Structure and function of Nucleic acids. DNA is composed of two sugar-phosphate backbones and nucleotide bases. Learning centers handbooks protocols scientific posters citations get support.
They carry the genetic blueprint of a cell and carry instructions for the functioning of the cell. Enroll Today Dive Deep into the World of Biology. If all the DNA in a typical mammalian cell were stretched out end to end it would extend more than 2 m.
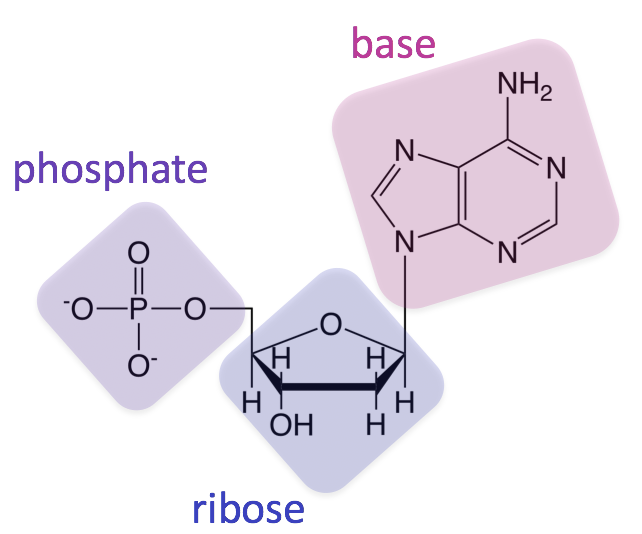
The monomeric unit of nucleic acids are nucleoside monophosphates. Nucleic acids deoxyribonucleic acid DNA and ribonucleic acid RNA carry genetic information which is read in cells to make the RNA and proteins by which living things function. Nucleic acids are long-chain polymeric molecules the monomer the repeating unit is known as the nucleotides and hence sometimes nucleic acids are referred to as polynucleotides.
The energy released by the. Nucleic Acids Store and Retrieve Genetic Information Biology Place Tutorial 4. Nucleic acids are large polymers formed by linking nucleotides together and are found in every cell.
Biochemistry 4e Chapter 33 331-335 Practice Questions. The two main types of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid DNA and ribonucleic acid RNA. Extraction clean up detection.
To be able to describe the structure and function of lipids nucleic acids carbohydrates and proteins. Deoxyribonucleic acid DNA is the nucleic acid that stores genetic information. Nucleotide Primary Structure A quick review.
When nucleic acids are hydrolyzed nucleoside monophosphates result. - nucleic acids are the carrier of genetic information and have a structure that is suited to that function - there are two main types of nucleic acids. Sugars There are only two types of sugar present in nucleic acids ribose which.
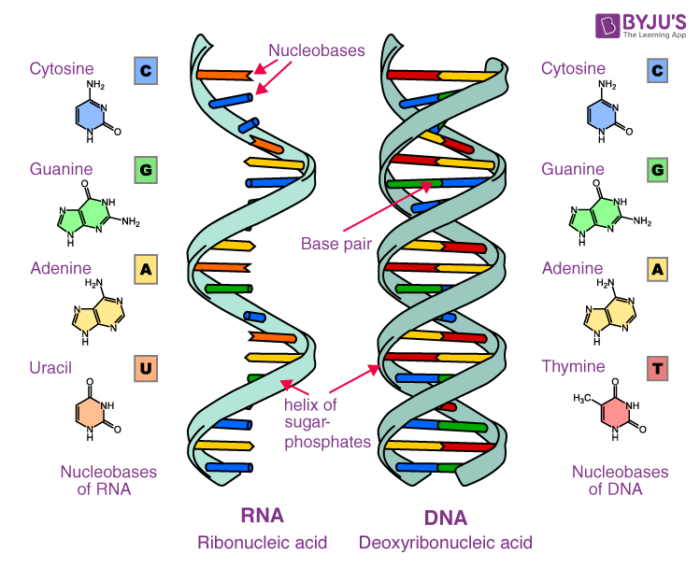
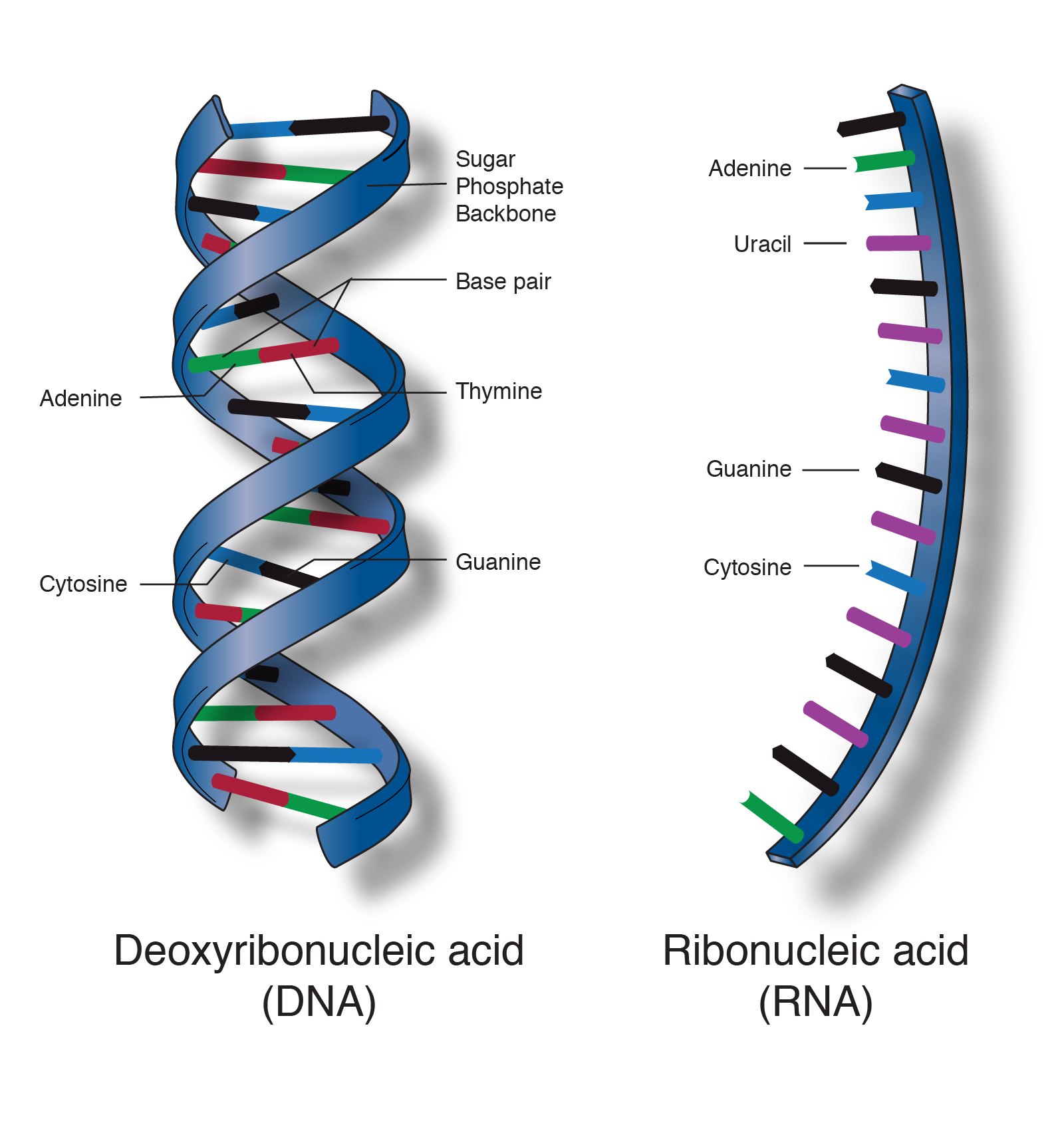
DNA and RNA characteristic DNA RNA sugar deoxyribose ribose Number of strands Double-stranded Single-stranded base ATCG AUCG - each type of nucleic acid consists of a sugar-phosphate backbone the sugars and phosphates. Describe the structure and function of lipids nucleic acids carbohydrates and proteins. Describe the structures of DNA molecules in terms of backbone grooves bases hydrogen bonding base pairing and packaging 3.
Show the relationship between lipids nucleic acids proteins and carbohydrates including the connection between their subunits and elements that make up the molecules. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. DNA and RNA are responsible for the inheritance and transmission of specific characteristics.
The DNA molecules never leave the nucleus but instead use an RNA intermediary to. Describe the structure of the nucleic acid polymer a purine or pyrimidine nucleobase a pentose sugar and a phosphate group. Describe how a deoxyribose to ribose changes the structure and function of a nucleic acid.
DNA is a double-stranded molecule organized into chromosome found in. Nucleic acids are the most important macromolecules for the continuity of life. The two main types of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid DNA and ribonucleic acid RNA.
Nucleic Acids Structure These vital macromolecules are typically made of oxygen nitrogen hydrogen phosphorus and most importantly carbon. Function of Nucleic Acids The purpose of DNA is to act as a code or recipe for making proteins. 10-13 15 17 Learning Objectives.
The well-known structure of the DNA double helix allows this information to be copied and passed on to the next generation. ACTIVITY 1 Cartoon Make a cartoon or comic that tells a. Nucleotides of Nucleic Acids.
Deoxy-ribonucleic acid DNA and ribonucleic acid RNA. Both DNA and RNA have been shown to consist of three groups of molecules. Ad Comprehensive Biology Course.
Nucleic Acids - Structure and Function DNA and RNA in Cells. Deoxyribonucleic acid DNA and ribonucleic acid RNA are two major types of nucleic acids. Nucleic acids are long linear polymers of nucleotides.
Distinguish between nucleosides and nucleotides 2. DNA is the genetic material found in all living organisms ranging from single-celled bacteria to multicellular mammals. The other type of nucleic acid RNA is mostly involved in protein synthesis.
Basically nucleic acids can be subdivided into two types. Nucleic Acids Function The DNA never leaves its place of origin but uses the RNA to act as an intermediate to communicate with the rest of the cell. Nucleoside triphosphates are the precursors for the synthesis nucleic acids.
Describe the structures of RNA molecules in terms of. Describe the basic structure of nucleic acids. To be able to show the relationship between lipids nucleic acids proteins and carbohydrates including the connection between their subunits and elements that make up the molecules.
Comments
Post a Comment